What is Aerogel?
-
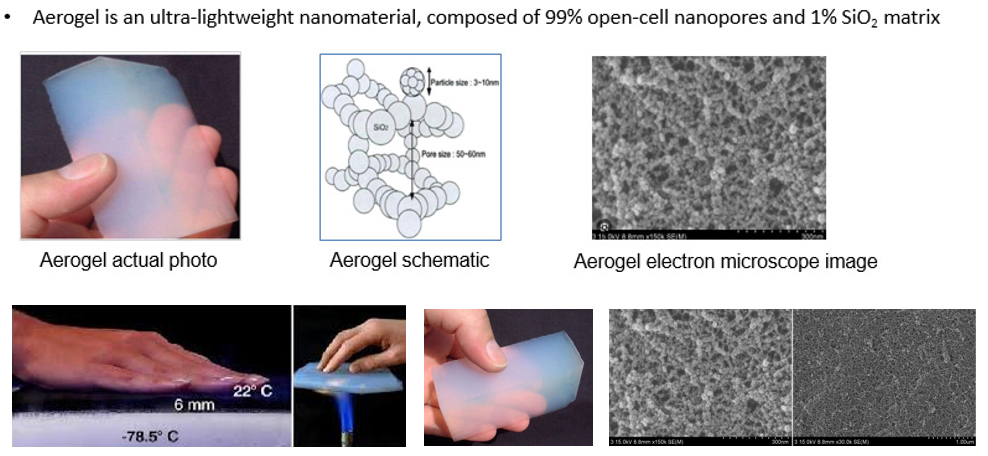
Aerogel is an extraordinary material known for its unique properties and versatile applications. It is composed of over 90% air by volume, with this air residing in extremely small nanopores. The remaining structure consists of a three-dimensional network of interconnected silica solid clusters, making aerogel both the lightest solid material known and the most effective insulator.Aerogel is an extraordinary, ultra-lightweight material with unique properties and versatile applications. It is created by replacing the liquid component of a traditional gel with gas, resulting in a structure that is over 90% air by volume. This air resides in extremely small nanopores, while the remaining structure consists of a three-dimensional network of interconnected silica solid clusters. This composition makes aerogel one of the lightest solid materials known and the most effective insulator available.
The aerogel’s structure is characterized by an open-celled, mesoporous network of interconnected nanostructures. The pores, which range from 2 to 50 nanometers in diameter, trap gas within, significantly reducing heat transfer. This network of nanopores minimizes conduction, convection, and radiation, allowing aerogel to excel in thermal insulation. The Knudsen effect, where gas molecules within small pores have limited movement, further enhances aerogel's insulating performance.
Despite their fragile appearance, aerogels are surprisingly strong due to their three-dimensional porous network. Their properties, including density, transparency, mechanical strength, and thermal conductivity, can be precisely controlled through the production process. For instance, silica aerogels are often transparent with a bluish tint, while carbon aerogels are black and more electrically conductive.
Key Properties
Aerogels exhibit several exceptional characteristics, including:
-
Low DensityAerogels are among the lightest solid materials, with some formulations having a density as low as 0.0011 g/cm³.
-
Thermal InsulationAerogels are highly effective thermal insulators, thanks to their porous structure, which minimizes both conductive and convective heat transfer.
-
High Surface AreaAerogels have a large specific surface area, up to 3200 m²/g, making them ideal for applications in filtration and catalysis.
-
Mechanical StrengthDespite their low density, aerogels can bear significant loads due to their dendritic structure, although they may be brittle under extreme pressure.
-
Hydrophilicity and HydrophobicityAerogels are naturally hydrophilic, meaning they absorb moisture, but can be treated chemically to become hydrophobic, protecting their structure from water-induced degradation
Applications
Aerogels are used in a wide range of industries, including:
-
Thermal InsulationDue to their excellent thermal properties, aerogels are commonly used in aerospace applications, such as insulating spacecraft and space suits, as well as in industrial settings, including LNG storage and high-energy piping.
-
Energy EfficiencyAerogels improve energy efficiency in various systems, such as refining plants, petrochemical facilities, and district heating systems.
-
Consumer ProductsAerogels are also utilized in products like insulated jackets and protective clothing, where their lightweight yet effective insulation is highly valued.
-
Environmental FiltrationThe high surface area of aerogels makes them suitable for environmental applications such as filtration and pollutant removal.
LHJ Global has pioneered an innovative production method, the "Gradual Pressure-Relief Drying Process," which has significantly reduced the cost of manufacturing aerogels. This breakthrough allows for the large-scale production and industrial application of aerogels at a lower cost, making these advanced materials more accessible to various industries. Through this technology, LHJ Global is providing high-performance aerogel products to customers worldwide, backed by numerous international patents.

 KOR
KOR ENG
ENG